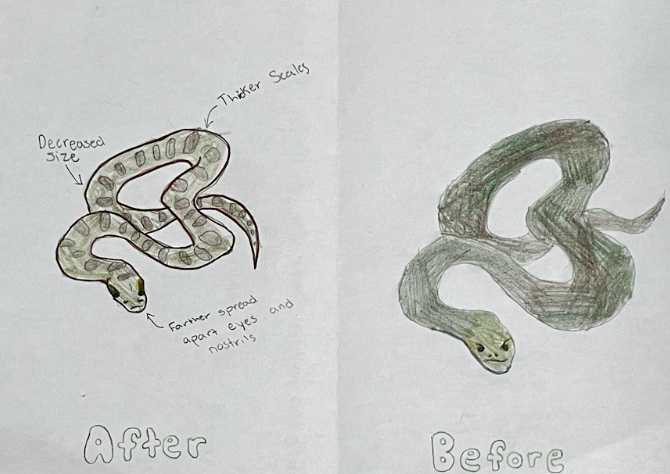
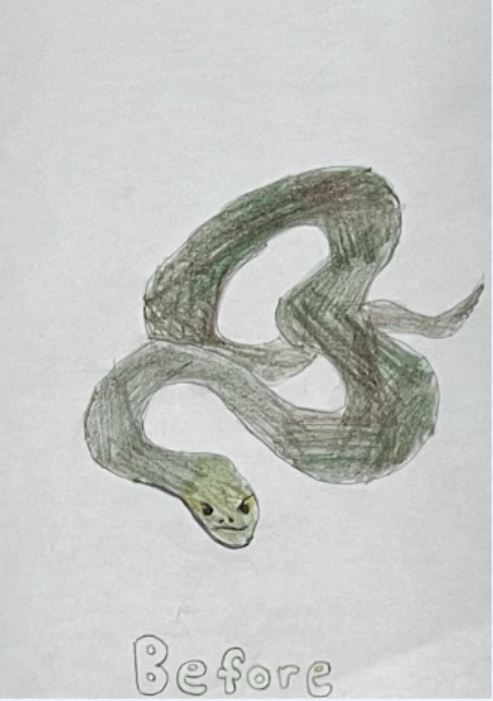
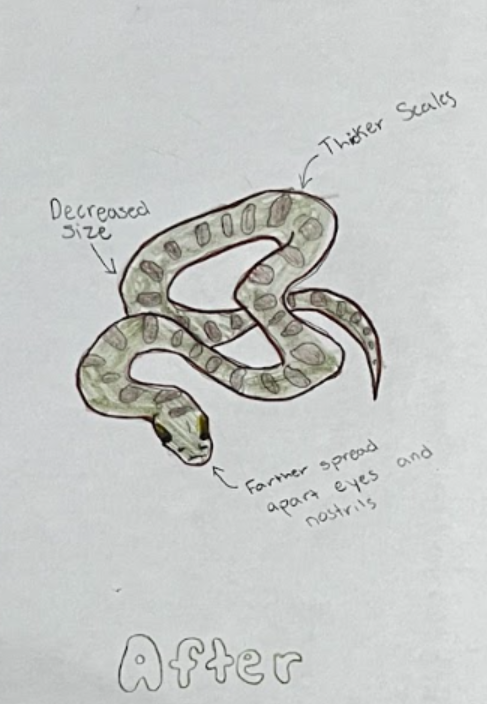
Green anacondas are a unique and adaptable species that thrive in wet, dense vegetation. Their olive-green color and pattern provide camouflage and are well-adapted to aquatic life. However, climate change could lead to habitat loss and population decline due to increased drought conditions in rainforest environments. As temperatures rise, rainfall patterns can change, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, significantly impacting their aquatic habitats. This can cause them to develop thicker scales because they will have to move towards drier habitats. This will impact their look by starting to grow eyes and nostrils on the side of its head, for a wider sight range. Additionally, the animals they prey on may shift their ranges, making it harder for green anacondas to find food. Extreme temperature fluctuations can disrupt thermoregulation, potentially leading to anacondas learning to eat vegetarian and decreasing in size.
Contact us
Thank you for your interest in contacting Future Engineers. We look forward to connecting with you!
General Inquiries
support@futureengineers.orgSponsorship Inquiries
sponsor@futureengineers.org