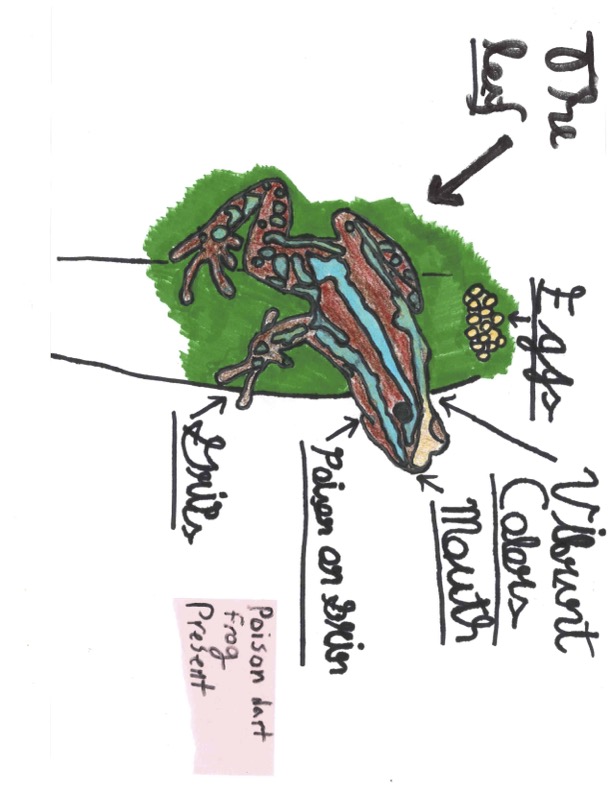
The poison dart frog (Dendrobatidae) is a small, brightly colored amphibian found in the rainforests of Central and South America, measuring 2.5 inches. Their vibrant yellow, blue, green, and red skin warns predators of their toxins, from alkaloids in their insect diet. These frogs are often seen perched on leaves, and females lay eggs in water-filled plant pockets for tadpoles. They play a vital role in their ecosystem, highlighting the diversity of rainforest life. The future frog stands out with bright colors, signaling danger to predators. They can glide, extending their legs and carrying eggs on their backs to keep them moist. Some species can self-fertilize, allowing both males and females to contribute to reproduction. Like gobies, these frogs don't strictly adhere to traditional gender roles. Their defenses include false eyes to deter attacks and the ability to spit poison. These adaptations highlight their unique role in the ecosystem.
Contact us
Thank you for your interest in contacting Future Engineers. We look forward to connecting with you!
General Inquiries
support@futureengineers.orgSponsorship Inquiries
sponsor@futureengineers.org