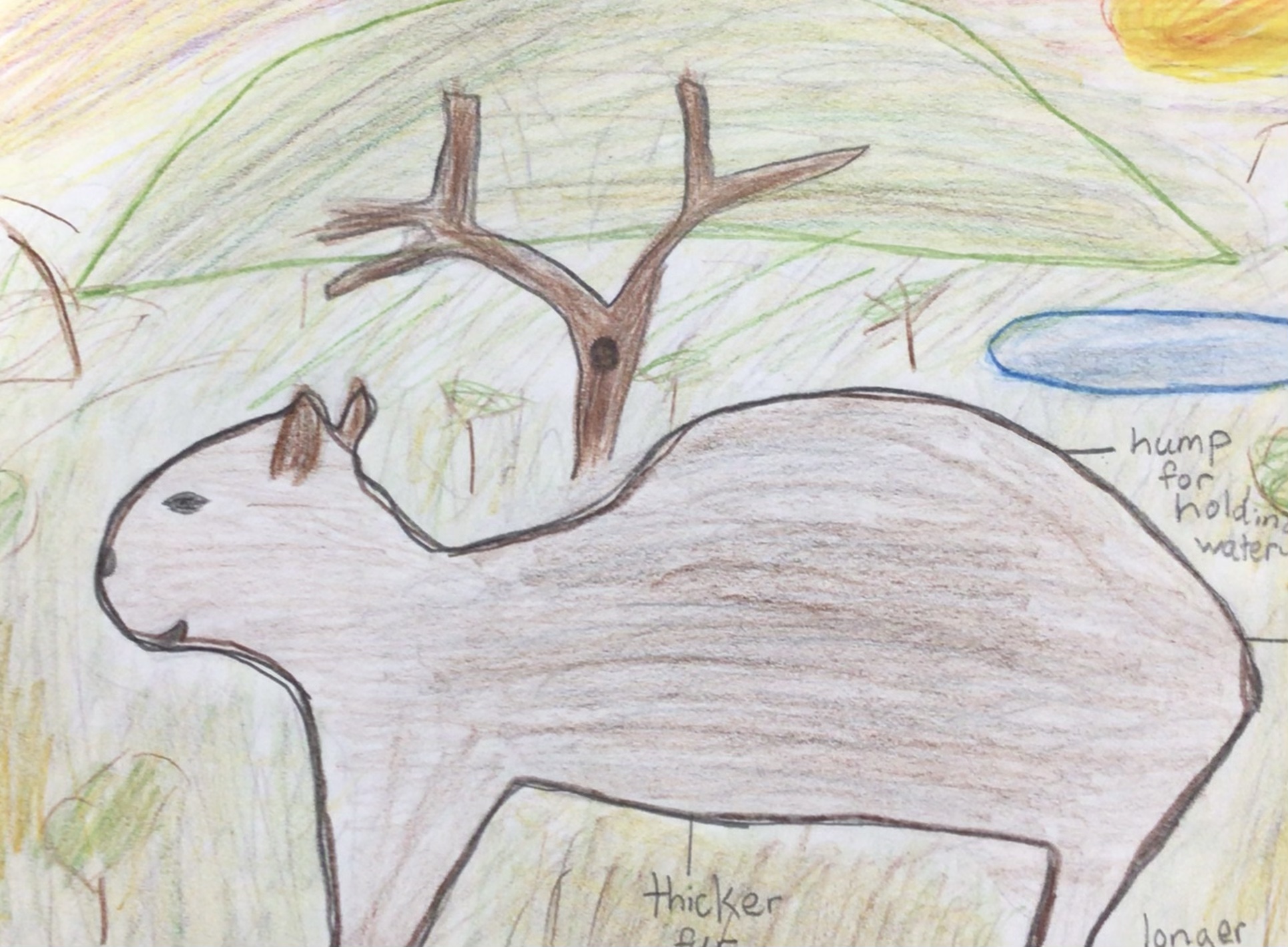
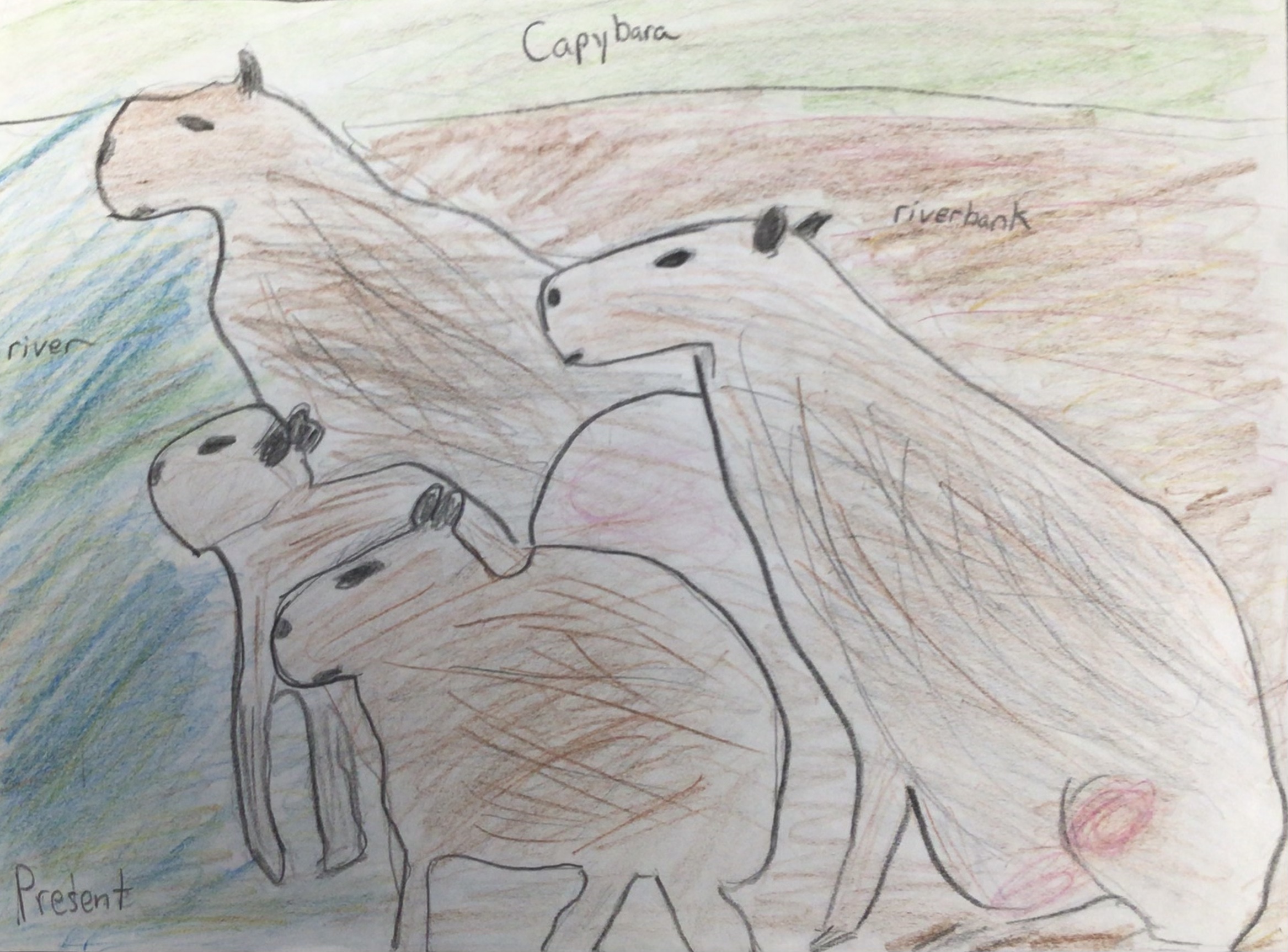
The capybara’s current habitat is the dense rainforests in central South America. Capybaras are 2 feet tall, can weigh up to 150 pounds, and eat grasses and water plants. Groups of ten live by rivers and ponds. They’ve adapted to water by holding their breath for 5 minutes. Main threats include jaguars, deforestation, illegal poaching, and habitat destruction. Deforestation and global warming could cause the capybara’s habitat to become a dry savanna biome. The water dependent capybara would need adaptations of a hump to carry water and skin that is more efficient at retaining moisture. Feet more adapted to running would help them escape predators in their new more open habitat. A coat to help them stay cool in the hotter and drier environment. Scientists predict that the rainforest could turn into savannas by 2050 and animals take one million years for the capybara to evolve with new traits.
Contact us
Thank you for your interest in contacting Future Engineers. We look forward to connecting with you!
General Inquiries
support@futureengineers.orgSponsorship Inquiries
sponsor@futureengineers.org