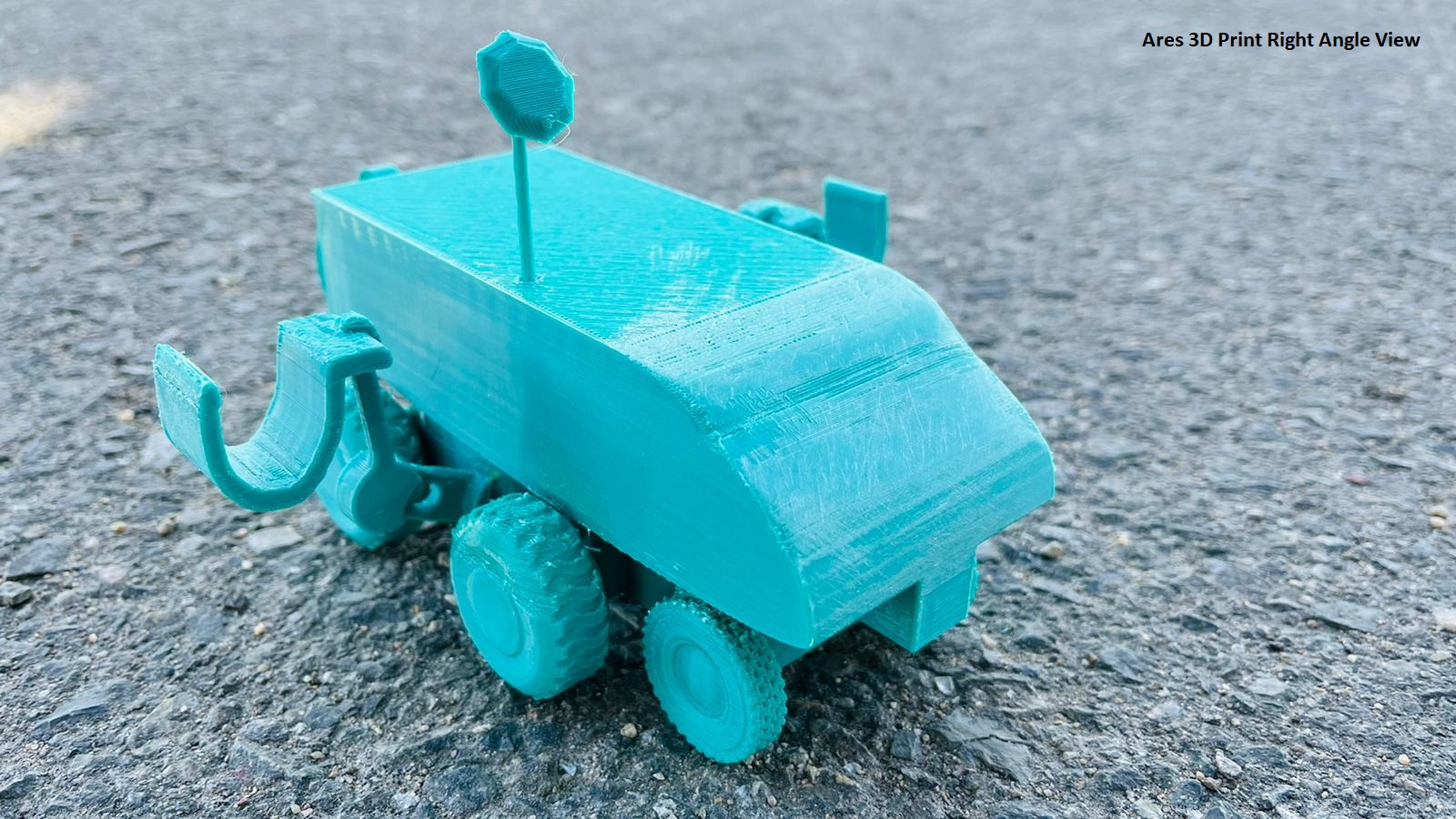
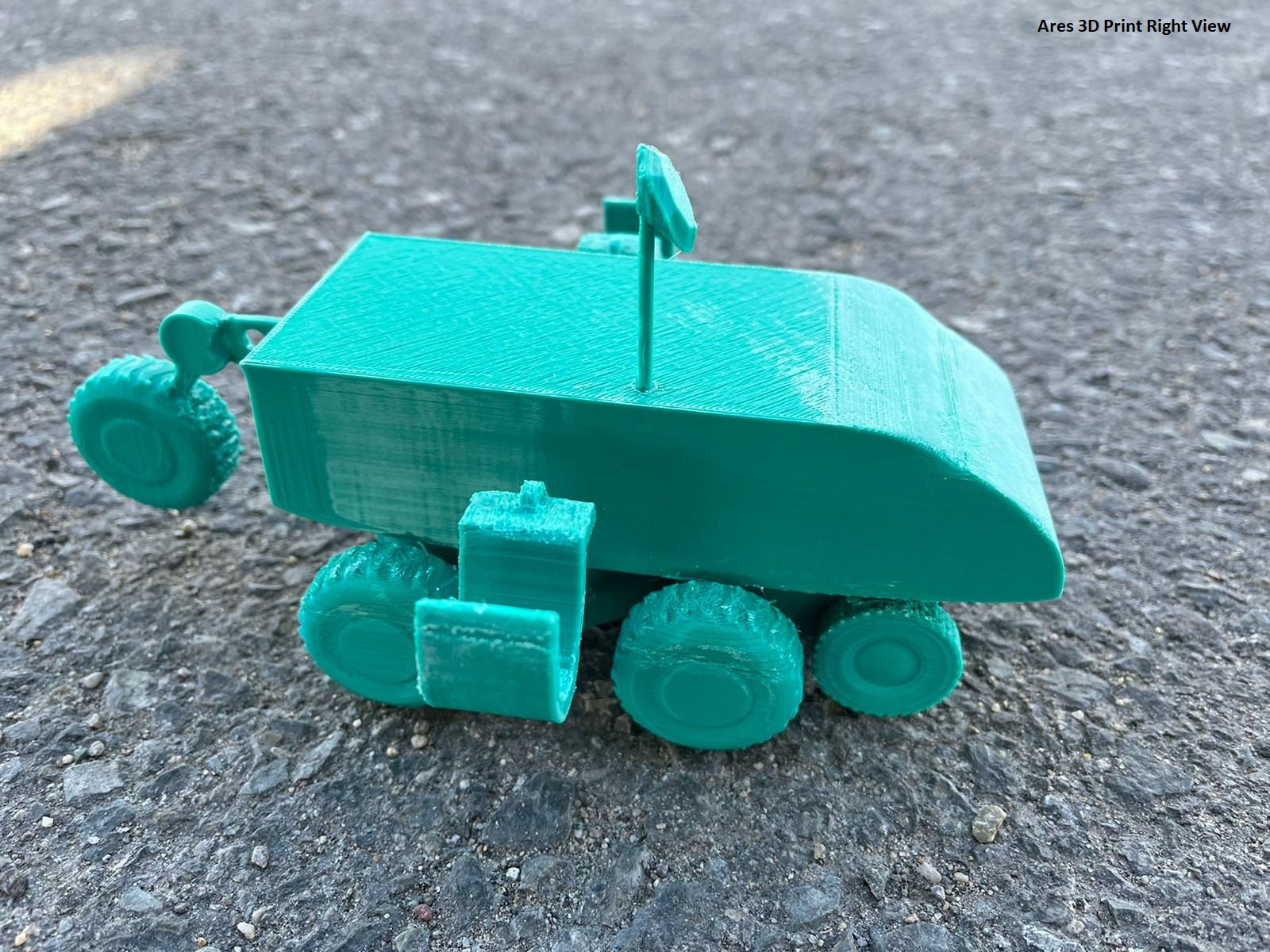
Ares, powered by Lithium-ion batteries is designed to transport more regolith per trip with fewer trips. After collecting an adequate amount of regolith or having manual callback signaled, Ares will use its satellite to navigate to base. Ares sports four metal wheels rather than treads which are prone to jamming and two wheels in the front to distribute weight. If Ares gets stuck, there’s a seventh wheel in the back which allows Ares to wheelie and get out of a ditch. The extreme conditions on our moon require durable materials like aluminum alloy and titanium which encase Ares. Ares features a camera and a flashlight for use by base personnel. It has a laser-based sensor which approximates regolith density by evaluating the reflection of the laser. Ares scoops up regolith with claws if the density is high, or else it vacuums the regolith with indium-tin-oxide coated vacuum to prevent buildup.
Contact us
Thank you for your interest in contacting Future Engineers. We look forward to connecting with you!
General Inquiries
support@futureengineers.orgSponsorship Inquiries
sponsor@futureengineers.org