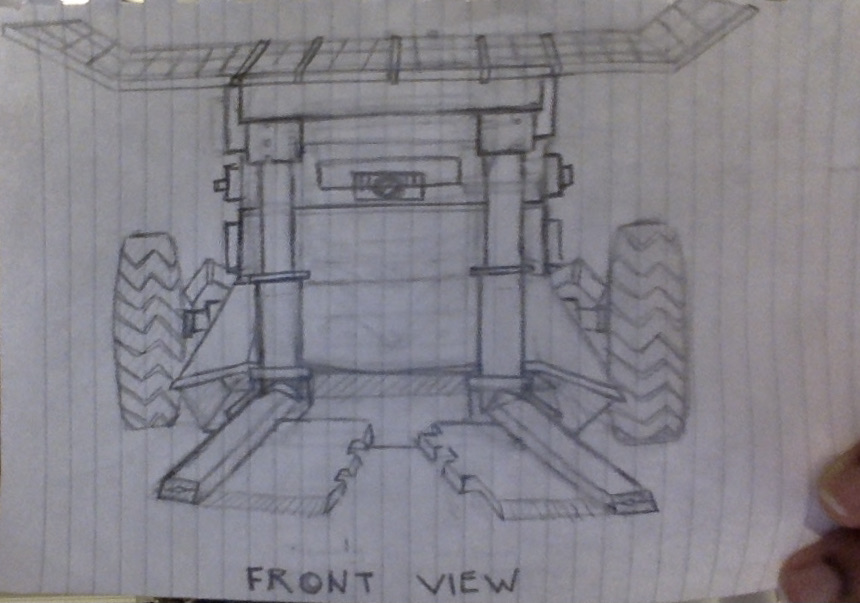
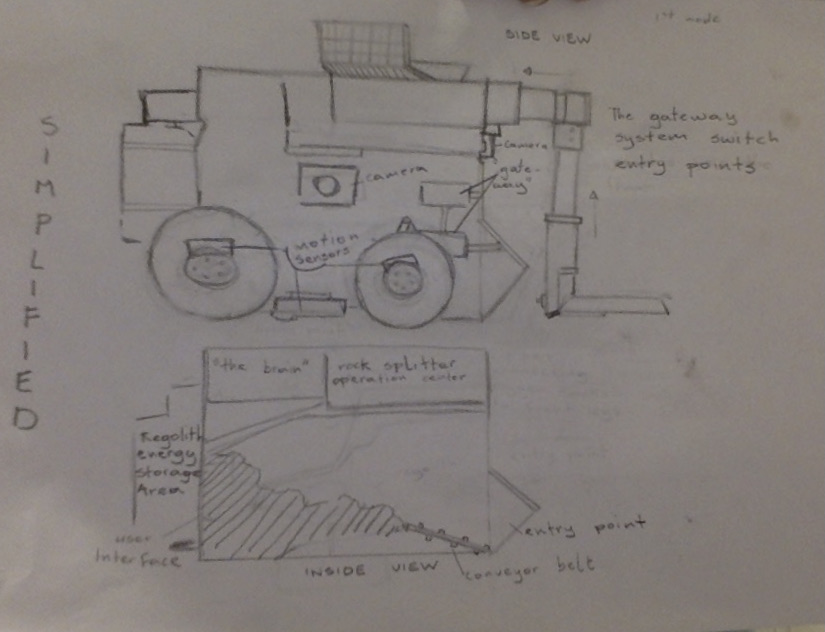
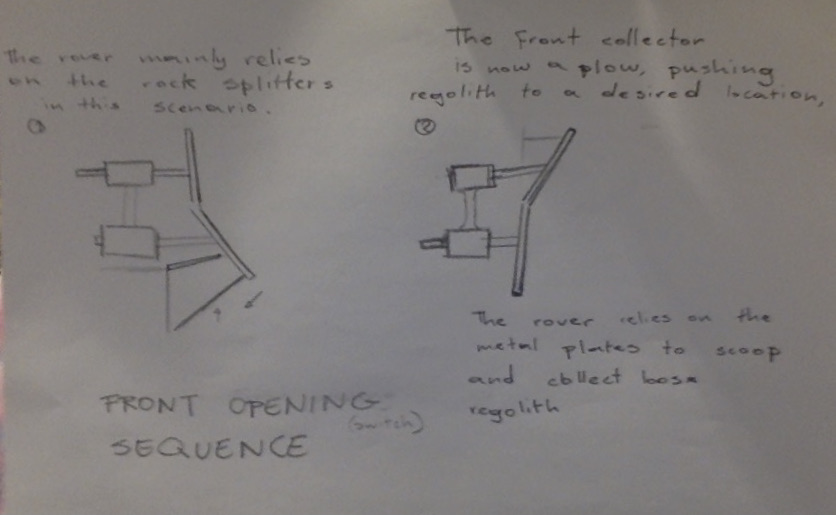
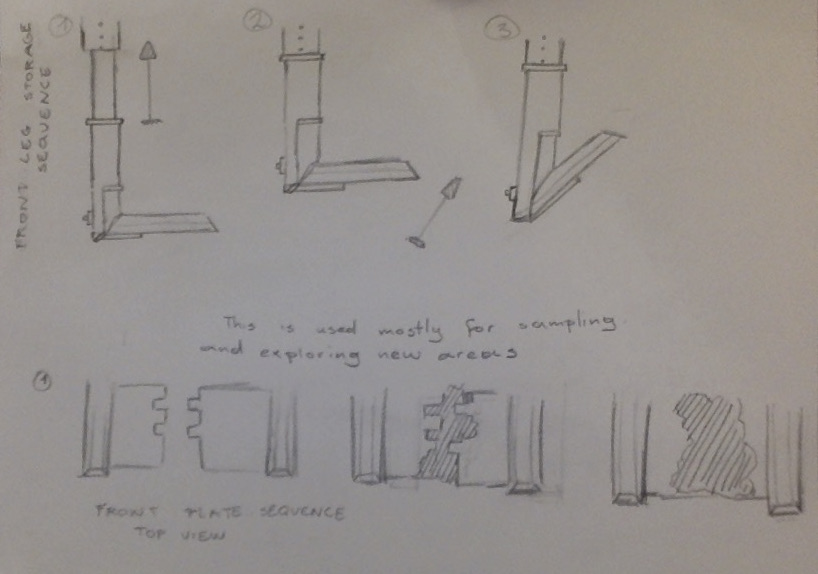
The rover receives orders and mission plans from a mission control group on the moon. It uses satellite images and a 3d mapping system to plan routes and passages. The rover is mainly made of titanium, aluminum, and copper, the exterior coated with a thin mixture of tungsten and glass. The front wheels are paired with extendable strut dust boots that are visible on the outside and add stability to the rover, allowing it to execute crater-bound missions with ease. All of the electronics are insulated and have heat-reflective exteriors. The device is also equipped with hydraulic rock splitters and metal plates at the front. There are two possible entry points for the regolith depending on what mode of operation is used and the nature of the mission. The rover is solar-powered but uses regolith for stored energy. The rover uses motion detectors and cameras to evaluate the terrain.
Contact us
Thank you for your interest in contacting Future Engineers. We look forward to connecting with you!
General Inquiries
support@futureengineers.orgSponsorship Inquiries
sponsor@futureengineers.org